| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
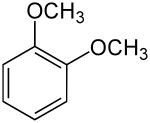
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-Dimethoxybenzene[1] | |
| Other names
Veratrole
o-Dimethoxybenzene Pyrocatechol dimethyl ether | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.860 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 138.166 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.084 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | 22–23 °C (72–73 °F; 295–296 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 206–207 °C (403–405 °F; 479–480 K)[2] |
| -87.39·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302 | |
| P264, P270, P301+P312, P330, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1,2-Dimethoxybenzene, commonly known as veratrole, is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(OCH3)2. It is one of three isomers of dimethoxybenzene. It is a colorless liquid, with a pleasant odor and slight solubility in water. It is the dimethyl ether derived from pyrocatechol.
- ^ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 702. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-00648. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c Merck Index, 11th Edition, 9857
