| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3,5-Trithiane | |||
| Other names
Thioformaldehyde trimer, Trimethylentrisulfide, Trimethylene trisulfide, Trithioformaldehyde, 1,3,5-Trithiacyclohexane, sym-Trithiane, Thioform, s-Trithiane
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.482 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H6S3 | |||
| Molar mass | 138.27 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless solid | ||
| Density | 1.6374 g/cm3[1] | ||
| Melting point | 215 to 220 °C (419 to 428 °F; 488 to 493 K) | ||
| Slightly soluble | |||
| Solubility | Benzene | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Toxic (T) | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H319 | |||
| P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P313 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
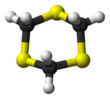
1,3,5-Trithiane is the chemical compound with the formula (CH2S)3. This heterocycle is the cyclic trimer of the otherwise unstable species thioformaldehyde. It consists of a six-membered ring with alternating methylene bridges and thioether groups. It is prepared by treatment of formaldehyde with hydrogen sulfide.[2]
Trithiane is a building block molecule in organic synthesis, being a masked source of formaldehyde. In one application, it is deprotonated with organolithium reagents to give the lithium derivative, which can be alkylated.[3]
- (CH2S)3 + RLi → (CH2S)2(CHLiS) + RH
- (CH2S)2(CHLiS) + R′Br → (CH2S)2(CHR′S) + LiBr
- (CH2S)2(CHR′S) + H2O → R′CHO + ....
Trithiane is the dithioacetal of formaldehyde. Other dithioacetals undergo similar reactions to the above.
It is also a precursor to other organosulfur reagents. For example, chlorination in the presence of water affords the chloromethyl sulfonyl chloride:[4]
- (CH2S)3 + 9 Cl2 + 6 H2O → 3 ClCH2SO2Cl + 12 HCl

- ^ David R. Lide, ed. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 85th Edition, Internet Version 2005. CRC Press, 2005.
- ^ Bost, R. W.; Constable, E. W. "sym-Trithiane" Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 2, p.610 (1943). http://orgsyn.org/Content/pdfs/procedures/CV2P0610.pdf
- ^ Seebach, D.; Beck, A. K. "Aldehydes From sym-Ttrithiane: n-Pentadecanal" Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 6, p.869 (1988). http://orgsyn.org/Content/pdfs/procedures/CV6P0869.pdf
- ^ Paquette, L. A.; Wittenbrook, L. S. "2-Chlorothiirane 1,1-Dioxide" Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 5, p.231 (1973). http://orgsyn.org/Content/pdfs/procedures/CV5P0231.pdf