| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butan-1-ol[1] | |||
| Other names
n-Butanol
n-Butyl alcohol n-Butyl hydroxide n-Propylcarbinol n-Propylmethanol 1-Hydroxybutane Methylolpropane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 969148 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.683 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 25753 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | 1-Butanol | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1120 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H10O | |||
| Molar mass | 74.123 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless, refractive liquid | ||
| Odor | banana-like,[2] harsh, alcoholic and sweet | ||
| Density | 0.81 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −89.8 °C (−129.6 °F; 183.3 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 117.7 °C (243.9 °F; 390.8 K) | ||
| 73 g/L at 25 °C | |||
| Solubility | very soluble in acetone miscible with ethanol, ethyl ether | ||
| log P | 0.839 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 0.58 kPa (20 °C) ILO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 16.10 | ||
| −56.536·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3993 (20 °C) | ||
| Viscosity | 2.573 mPa·s (at 25 °C) [3] | ||
| 1.66 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
225.7 J/(K·mol) | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−328(4) kJ/mol | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−2670(20) kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 35 °C (95 °F; 308 K) | ||
| 343 °C (649 °F; 616 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 1.45–11.25% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
790 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
LDLo (lowest published)
|
3484 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 790 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1700 mg/kg (dog, oral)[5] | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
9221 ppm (mammal) 8000 ppm (rat, 4 h)[5] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 100 ppm (300 mg/m3)[4] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
C 50 ppm (150 mg/m3) [skin][4] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1400 ppm[4] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0111 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Butanethiol n-Butylamine Diethyl ether Pentane | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
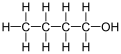
1-Butanol, also known as butan-1-ol or n-butanol, is a primary alcohol with the chemical formula C4H9OH and a linear structure. Isomers of 1-butanol are isobutanol, butan-2-ol and tert-butanol. The unmodified term butanol usually refers to the straight chain isomer.
1-Butanol occurs naturally as a minor product of the ethanol fermentation of sugars and other saccharides[6] and is present in many foods and drinks.[7][8] It is also a permitted artificial flavorant in the United States,[9] used in butter, cream, fruit, rum, whiskey, ice cream and ices, candy, baked goods, and cordials.[10] It is also used in a wide range of consumer products.[7]
The largest use of 1-butanol is as an industrial intermediate, particularly for the manufacture of butyl acetate (itself an artificial flavorant and industrial solvent). It is a petrochemical derived from propylene. Estimated production figures for 1997 are: United States 784,000 tonnes; Western Europe 575,000 tonnes; Japan 225,000 tonnes.[8]
- ^ "1-Butanol - Compound Summary". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center of Biotechnology Information.
- ^ [n-Butanol Product Information, The Dow Chemical Company, Form No. 327-00014-1001, page 1]
- ^ Dubey, Gyan (2008). "Study of densities, viscosities, and speeds of sound of binary liquid mixtures of butan-1-ol with n-alkanes (C6, C8, and C10) at T = (298.15, 303.15, and 308.15) K". The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics. 40 (2): 309–320. doi:10.1016/j.jct.2007.05.016.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0076". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b "N-butyl alcohol". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Hazelwood, Lucie A.; Daran, Jean-Marc; van Maris, Antonius J. A.; Pronk, Jack T.; Dickinson, J. Richard (2008), "The Ehrlich pathway for fusel alcohol production: a century of research on Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism", Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 74 (8): 2259–66, Bibcode:2008ApEnM..74.2259H, doi:10.1128/AEM.02625-07, PMC 2293160, PMID 18281432.
- ^ a b Butanols: four isomers, Environmental Health Criteria monograph No. 65, Geneva: World Health Organization, 1987, ISBN 92-4-154265-9.
- ^ a b n-Butanol (PDF), SIDS Initial Assessment Report, Geneva: United Nations Environment Programme, April 2005.
- ^ 21 C.F.R. § 172.515; 42 FR 14491, Mar. 15, 1977, as amended.
- ^ Hall, R. L.; Oser, B. L. (1965), "Recent progress in the consideration of flavouring ingredients under the food additives amendment. III. Gras substances", Food Technol.: 151, cited in Butanols: four isomers, Environmental Health Criteria monograph No. 65, Geneva: World Health Organization, 1987, ISBN 92-4-154265-9.


