| 1948 Atlantic hurricane season | |
|---|---|
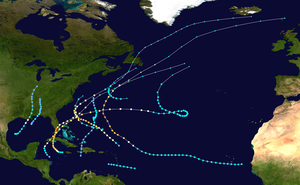 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | April 15, 1948 |
| Last system dissipated | November 11, 1948 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Six and Eight |
| • Maximum winds | 130 mph (215 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 940 mbar (hPa; 27.76 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 15 |
| Total storms | 10 |
| Hurricanes | 6 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 4 |
| Total fatalities | 112 |
| Total damage | $28.8 million (1948 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 1948 Atlantic hurricane season featured the first tropical cyclone before the month of June since 1940.[1] The season officially began on June 15, 1948, and lasted until November 15, 1948. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. There were fifteen tropical cyclones; ten systems strengthened into a tropical storm, six storms attained hurricane status, and four storms intensified into major hurricanes, which are Category 3 or higher on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale.[2] Operationally, it was believed that a weak tropical disturbance formed over the southeast Bahamas in May and moved northwest into the Georgia coast near Savannah. This system was later excluded from HURDAT. The seventh tropical cyclone was not operationally considered a tropical cyclone, but was later added to HURDAT.
The sixth and eighth systems, designated as Dog and Easy by the Air Weather Service in real time,[nb 1] respectively, were the most intense tropical cyclones of the season, peaking as a Category 4 hurricane with a minimum barometric pressure of 940 mbar (27.76 inHg). The former caused eight deaths and $400,000 (1948 USD)[nb 2] in damage after bringing strong winds, rough seas, and heavy rainfall to Bermuda and Atlantic Canada. In Cuba and Florida, the eighth hurricane left 13 fatalities and at least $14 million in damage. The ninth hurricane, assigned the name Fox by the Air Weather Service, brought similar impact to Cuba and Florida about two weeks later. In May, the first tropical cyclone killed 80 people from flooding in the Dominican Republic. Collectively, the storms of this season left around $28.8 million in damage and 112 fatalities.
- ^ "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved November 15, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ACEwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Report on the 1948-49 Post-Analysis Program of the Air Force Hurricane Office (Air Weather Service Technical Report). Washington, D.C.: United States Air Weather Service. 1949.
- ^ Roth, David M. (November 25, 2012). "CLIQR tropical cyclone database". Hydrometrological Prediction Center. College Park, Maryland: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on October 6, 2012. Retrieved June 27, 2024.
Cite error: There are <ref group=nb> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=nb}} template (see the help page).