| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
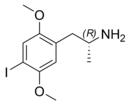
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(4-Iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)propan-2-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H16INO2 | |
| Molar mass | 321.1558 g/mol |
| Melting point | 201.5 °C (394.7 °F; 474.6 K) (hydrochloride) |
| 10 mg/mL[1] | |
| Pharmacology | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine (DOI) is a psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. Unlike many other substituted amphetamines, however, it is not primarily a stimulant.[3] DOI has a stereocenter and R-(−)-DOI is the more active stereoisomer. In neuroscience research, [125I]-R-(−)-DOI is used as a radioligand and indicator of the presence of 5-HT2A serotonin receptors. DOI's effects have been compared to LSD, although there are differences that experienced users can distinguish. Besides the longer duration, the trip tends to be more energetic than an LSD trip, with more body load and a different subjective visual experience. The after effects include residual stimulation and difficulty sleeping, which, depending on the dose, may persist for days.[3] While rare, it is sometimes sold as a substitute for LSD, or even sold falsely as LSD, which may be dangerous because DOI does not have the same established safety profile as LSD.[4]
- ^ "D101 DOI hydrochloride ≥98% (HPLC), solid". Retrieved 13 April 2008.
- ^ Anvisa (2023-07-24). "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-07-25). Archived from the original on 2023-08-27. Retrieved 2023-08-27.
- ^ a b Shulgin, A; Shulgin, A (1990). "#67 DOI". PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Transform Press. ISBN 978-0963009609. Archived from the original on 2014-10-27. Retrieved 2014-12-17.
- ^ "LSD Blotter Acid Mimics (Actually containing 4-IODO-2,5-DIMETHOXYAMPHETAMINE (DOI) and 4-CHLORO-2,5-DIMETHOXYAMPHETAMINE (DOC)) in Lantana, Florida". DEA Microgram Bulletin. Washington, DC: Office of Forensic Sciences, Drug Enforcement Administration. June 2008. Archived from the original on 2009-02-04. Retrieved 12 February 2009.