| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Ethylhexan-1-ol[1] | |
| Other names
isooctyl alcohol, 2-ethylhexanol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1719280 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.941 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 2-ethylhexanol |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
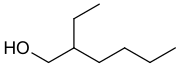
| CH3CH2CH2CH2CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH | |
| Molar mass | 130.231 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 833 mg/mL |
| Melting point | −76 °C (−105 °F; 197 K) |
| Boiling point | 180 to 186 °C; 356 to 367 °F; 453 to 459 K |
| log P | 2.721 |
| Vapor pressure | 30 Pa (at 20 °C) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.431 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
317.5 J/(K·mol) |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
347.0 J/(K·mol) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−433.67–−432.09 kJ/mol |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−5.28857–−5.28699 MJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Mildly toxic |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H312, H315, H318, H335 | |
| P261, P280, P305+P351+P338 | |
| Flash point | 81 °C (178 °F; 354 K) |
| 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 0.88–9.7% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
|
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 50 ppm (270 mg/m3) (skin)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanol
|
Propylheptyl alcohol |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2-Ethylhexanol (abbreviated 2-EH) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CH2CH2CH2CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH. It is a branched, eight-carbon chiral alcohol. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It is produced on a large scale (>2,000,000,000 kg/y) for use in numerous applications such as solvents, flavors, and fragrances and especially as a precursor for production of other chemicals such as emollients and plasticizers.[3] It is encountered in plants, fruits, and wines.[4][5] The odor has been reported as "heavy, earthy, and slightly floral" for the R enantiomer and "a light, sweet floral fragrance" for the S enantiomer.[6][7]
- ^ "2-ethylhexanol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 29 January 2012.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0354". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
ROHwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Fan, Wenlai; Qian, Michael C. (2006). "Characterization of Aroma Compounds of Chinese "Wuliangye" and "Jiannanchun" Liquors by Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 54 (7): 2695–2704. doi:10.1021/jf052635t. PMID 16569063.
- ^ Mayuoni-Kirshinbaum, Lina; Tietel, Zipora; Porat, Ron; Ulrich, Detlef (2012). "Identification of aroma-active compounds in 'wonderful' pomegranate fruit using solvent-assisted flavour evaporation and headspace solid-phase micro-extraction methods". European Food Research and Technology. 235 (2): 277–283. doi:10.1007/s00217-012-1757-0. S2CID 97102092.
- ^ Klaus Rettinger; Christian Burschka; Peter Scheeben; Heike Fuchs; Armin Mosandl (1991). "Chiral 2-alkylbranched acids, esters and alcohols. Preparation and stereospecific flavour evaluation" (PDF). Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2 (10): 965–968. doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(00)86137-6.
- ^ McGinty, D.; Scognamiglio, J.; Letizia, C.S.; Api, A.M. (2010). "Fragrance material review on 2-ethyl-1-hexanol". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 48: S115–S129. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.05.042. PMID 20659633.