 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Nexus, Venus, Bromo, Bees, Erox, Synergy, Performax or Toonies |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, insufflation, rectal |
| Drug class | Serotonergic psychedelic |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Liver, primarily metabolized by MAO-A and MAO-B |
| Metabolites | BDMPE, BDMPAA, BDMBA, and others |
| Onset of action | 20–40 min (oral) |
| Elimination half-life | 2.48 ± 3.20 h[1] |
| Duration of action | 4–12 hours depending on route of administration |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.088 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
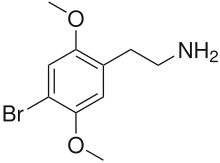
| Formula | C10H14BrNO2 |
| Molar mass | 260.131 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
2C-B (4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine), also known as Nexus, is a synthetic psychedelic drug of the 2C family, mainly used as a recreational drug.[2] It was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1974 for use in psychotherapy. To date, there is limited scientific information regarding the drug's pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects in humans. The existing studies primarily classify 2C-B as a stimulant and hallucinogen, and less commonly an entactogen and empathogen.[3]
2C-B, also referred to by a number of slang names, is known to circulate in the illicit market in multiple forms:[4][5] as a powder, in capsules or pills. For recreational use, the substance is generally consumed orally or nasally. In Shulgin's book PiHKAL, the oral dosage range is listed as 12–24 mg.[6]
- ^ Papaseit E, Farré M, Pérez-Mañá C, Torrens M, Ventura M, Pujadas M, et al. (2018). "Acute Pharmacological Effects of 2C-B in Humans: An Observational Study". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 9: 206. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00206. PMC 5859368. PMID 29593537.
- ^ Caudevilla-Gálligo F, Riba J, Ventura M, González D, Farré M, Barbanoj MJ, et al. (July 2012). "4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine (2C-B): presence in the recreational drug market in Spain, pattern of use and subjective effects". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 26 (7): 1026–1035. doi:10.1177/0269881111431752. PMID 22234927. S2CID 35535891.
- ^ González D, Torrens M, Farré M (2015-10-12). "Acute Effects of the Novel Psychoactive Drug 2C-B on Emotions". BioMed Research International. 2015: 643878. doi:10.1155/2015/643878. PMC 4620274. PMID 26543863.
- ^ "2C-B Street Names" (PDF). February 1, 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 16, 2012. Retrieved 2012-09-28.
- ^ Westhoff B (2019). Fentanyl, Inc. New York: Atlantic Monthly Press. p. 62. ISBN 978-1-0941-6390-1. OCLC 1136538402.
- ^ Shulgin AT (1991). Pihkal : a chemical love story. Ann Shulgin. Berkeley, CA: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628.