 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
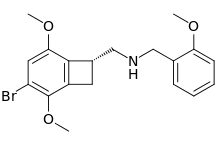
| Formula | C19H22BrNO3 |
| Molar mass | 392.293 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
2CBCB-NBOMe (NBOMe-TCB-2) is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine series of hallucinogens, which was discovered in 2007 at Purdue University as part of the ongoing research program of the team led by David Nichols focusing on the mapping of the specific amino acid residues responsible for ligand binding to the 5HT2A receptor. 2CBCB-NBOMe acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, with a Ki of 0.27 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, a similar potency to other agonists such as TCB-2, NBOMe-2C-I and Bromo-DragonFLY.[1]