| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
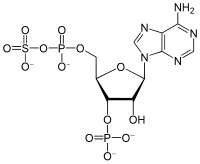
| IUPAC name
3′-O-Phosphono-5′-adenylyl hydrogen sulfate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methyl hydrogen (sulfooxy)phosphonate | |
| Other names
PAPS
3′-Phosphoadenylyl sulfate Phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate 3′-Phospho-5′-adenylyl sulfate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | PAPS |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.927 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H15N5O13P2S | |
| Molar mass | 507.266 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
3′-Phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphosulfate (PAPS) is a derivative of adenosine monophosphate (AMP) that is phosphorylated at the 3′ position and has a sulfate group attached to the 5′ phosphate. It is the most common coenzyme in sulfotransferase reactions and hence part of sulfation pathways.[1] It is endogenously synthesized by organisms via the phosphorylation of adenosine 5′-phosphosulfate (APS), an intermediary metabolite.[2] In humans such reaction is performed by bifunctional 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthases (PAPSS1 and PAPSS2) using ATP as the phosphate donor.[3][4]
- ^ Günal S; Hardman R; Kopriva S; Mueller JW (2019). "Sulfation pathways from red to green". J. Biol. Chem. 294 (33): 12293–12312. doi:10.1074/jbc.REV119.007422. PMC 6699852. PMID 31270211.
- ^ Negishi M; Pedersen LG; Petrotchenko E; et al. (2001). "Structure and function of sulfotransferases". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 390 (2): 149–57. doi:10.1006/abbi.2001.2368. PMID 11396917.
- ^ Xu, Zhen-Hua; Otterness, Diane M.; Freimuth, Robert R.; Carlini, Edward J.; Wood, Thomas C.; Mitchell, Steve; Moon, Eunpyo; Kim, Ung-Jin; Xu, Jing-Ping; Siciliano, Michael J.; Weinshilboum, Richard M. (February 2000). "Human 3′-Phosphoadenosine 5′-Phosphosulfate Synthetase 1 (PAPSS1) and PAPSS2: Gene Cloning, Characterization and Chromosomal Localization". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 268 (2): 437–444. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.2123. PMID 10679223.
- ^ Venkatachalam, K. V. (2003). "Human 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate (PAPS) synthase: Biochemistry, molecular biology and genetic deficiency". IUBMB Life. 55 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1080/1521654031000072148. PMID 12716056. S2CID 37733913.