| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
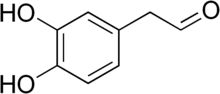
| Preferred IUPAC name
(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde | |
| Other names
DOPAL; 2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)acetaldehyde;[1] Dopaldehyde; Dopamine aldehyde
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| Abbreviations | DOPAL |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.237.172 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.149 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.306 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 351 °C (664 °F; 624 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related 2-phenyl aldehydes
|
Phenylacetaldehyde |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL), also known as dopamine aldehyde, is a metabolite of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine formed by monoamine oxidase (MAO).[2][3]
Other metabolic pathways of dopamine metabolism include methylation by catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) into 3-methoxytyramine and β-hydroxylation by dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) into norepinephrine. There is also spontaneous oxidation of dopamine into dopamine quinones and reactive oxygen species.[3]
- ^ "3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 24 June 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 13 October 2011.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Goldstein2020awas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Goldstein2021was invoked but never defined (see the help page).