| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Aminobenzoic acid | |||
| Other names
para-Aminobenzoic acid
p-Aminobenzoic acid PABA Vitamin B10 Vitamin Bx Bacterial vitamin H1 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.231 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H7NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 137.138 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White-grey crystals | ||
| Density | 1.374 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | 187 to 189 °C (369 to 372 °F; 460 to 462 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 340 °C (644 °F; 613 K) | ||
| 1 g/170 mL (25 °C) 1 g/90 mL (90 °C) | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
eye irritant, some persons may be allergic to this compound | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
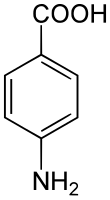
4-Aminobenzoic acid (also known as para-aminobenzoic acid or PABA because the two functional groups are attached to the benzene ring across from one another in the para position) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4CO2H. PABA is a white solid, although commercial samples can appear gray. It is slightly soluble in water. It consists of a benzene ring substituted with amino and carboxyl groups. The compound occurs extensively in the natural world.
- ^ van de Graaf, Bas (1981). "Substituent effects. 7. Microscopic dissociation constants of 4-amino- and 4-(dimethylamino)benzoic acid". J. Org. Chem. 46 (4): 653–657. doi:10.1021/jo00317a002.
- ^ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–89. ISBN 978-1-4987-5428-6.