| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Ursa Major |
| Right ascension | 13h 40m 44.27274s[2] |
| Declination | +54° 40′ 53.8860″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.69 - 4.75[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M2 III[4] |
| B−V color index | +1.630±0.006[5] |
| Variable type | SRb[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −18.61±0.20[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −19.418 mas/yr[2] Dec.: −10.63 mas/yr[2] |
| Parallax (π) | 5.5963 ± 0.1399 mas[2] |
| Distance | 580 ± 10 ly (179 ± 4 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.39[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.1[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 83.3±3.1[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 1,250[9] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 1.06±0.16[10] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,705±16[10] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.1±0.08[10] dex |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
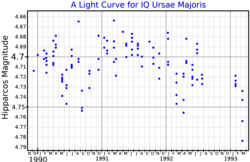
83 Ursae Majoris is a candidate binary star[12] system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is a semiregular variable star, and it has been given the variable star designation IQ Ursae Majoris. It ranges in brightness from apparent visual magnitude 4.69 to 4.75.[3] Percy and Au (1994) identified it as a small amplitude red variable with an irregular behavior, having a characteristic time scale of 20 days.[13] Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.60 mas,[2] it is located roughly 580 light years from the Sun. The system is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −18.6[6] km/s.
The visible component is an evolved red giant with a stellar classification of M2 III.[4] It is a marginal barium star, showing an enhanced abundance of s-process elements in its outer atmosphere. This material may have been acquired during a previous mass transfer from a now white dwarf companion, or self-enriched by a dredge-up during the asymptotic giant branch process.[14]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
HipDataAccesswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
DR3was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
Samus2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Keenan1989was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Anderson2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
DeBruijne2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Anders, F.; Khalatyan, A.; Chiappini, C.; Queiroz, A. B.; Santiago, B. X.; Jordi, C.; Girardi, L.; Brown, A. G. A.; Matijevič, G.; Monari, G.; Cantat-Gaudin, T.; Weiler, M.; Khan, S.; Miglio, A.; Carrillo, I.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Minchev, I.; de Jong, R. S.; Antoja, T.; Ramos, P.; Steinmetz, M.; Enke, H. (August 2019), "Photo-astrometric distances, extinctions, and astrophysical parameters for Gaia DR2 stars brighter than G = 18", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 628: A94, arXiv:1904.11302, Bibcode:2019A&A...628A..94A, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935765, ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Baines2023was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
chandler2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
MILESwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Eggleton2008was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Percy1994was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
gomez1997was invoked but never defined (see the help page).