| Acer floridanum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Young A. floridanum, about 4 m tall, showing color change. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Genus: | Acer |
| Section: | Acer sect. Acer |
| Series: | Acer ser. Saccharodendron |
| Species: | A. floridanum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acer floridanum | |
| |
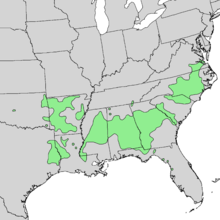
| Distribution | |
Acer floridanum (syn. Acer saccharum subsp. floridanum (Chapm.) Desmarais, Acer barbatum auct. non Michx.), commonly known as the Florida maple and occasionally as the southern sugar maple or hammock maple, is a tree that occurs in mesic and usually calcareous woodlands of the Atlantic and Gulf coastal plain in the United States, from southeastern Virginia in the north, south to central Florida, and west to Oklahoma and Texas and also common in south Illinois and Missouri[3][4][5]
- ^ NatureServe Explorer: Acer barbatum in NatureServe An online encyclopedia of life, Version 6.1. (2006). Arlington, Virginia.
- ^ Barstow, M.; Crowley, D. (2017). "Acer floridanum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T103451786A103451818. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T103451786A103451818.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Ward, D. B. (2004). Acer floridanum: The Correct Scientific Name of the Florida Maple. Castanea 69 (3): 230-233.
- ^ "Acer saccharum subsp. floridanum". Germplasm Resources Information Network. Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- ^ Jones Jr., Earle R (1990). "Acer barbatum". In Burns, Russell M.; Honkala, Barbara H. (eds.). Hardwoods. Silvics of North America. Vol. 2. Washington, D.C.: United States Forest Service (USFS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) – via Southern Research Station.

