| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
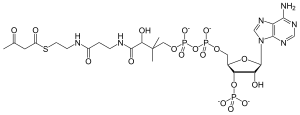
| IUPAC name
3′-O-Phosphonoadenosine 5′-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxo-4-{[3-oxo-3-({2-[(3-oxobutanoyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)propyl]amino}butyl dihydrogen diphosphate]
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methyl} O3-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxo-4-{[3-oxo-3-({2-[(3-oxobutanoyl)sulfanyl]ethyl}amino)propyl]amino}butyl] dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.378 |
| MeSH | acetoacetyl+CoA |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H40N7O18P3S | |
| Molar mass | 851.61 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis (ketogenesis) pathway of the liver.[1] In the ketone bodies digestion pathway (in the tissue), it is no longer associated with having HMG-CoA as a product or as a reactant.
It is created from acetyl-CoA, a thioester, which reacts with the enolate of a second molecule of acetyl-CoA in a Claisen condensation reaction,[2] and it is acted upon by HMG-CoA synthase to form HMG-CoA.[1] During the metabolism of leucine, this last reaction is reversed. Some individuals may experience Acetoacetyl-CoA deficiency.[3] This deficiency is classified as a disorder ketone body and isoleucine metabolism that can be inherited.[citation needed] Additional mutations include those with the enzymes within pathways related to Acetoacetyl CoA, including Beta-Ketothiolase deficiency and Mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Synthase mutation.

Additionally, it reacts with NADPH-dependent acetoacetyl-coenzyme A reductase, also known as PhaB, in a pathway that produces polyester polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The reduction of acetoacetyl-coA by Pha creates (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA, which polymerizes to PHA.[4] The pathway is present in bacteria such as Ralstonia eutropha and the PCC6803 strain of Synechocystis.[5] Mover over, Acetoacetyl-CoA is involved with neuronal development involving lipogenesis and providing fats and cholesterol for neuronal cells.
- ^ a b Hasegawa, Shinya; Noda, Kazuki; Maeda, Akina; Matsuoka, Masaru; Yamasaki, Masahiro; Fukui, Tetsuya (2012-11-01). "Acetoacetyl-CoA synthetase, a ketone body-utilizing enzyme, is controlled by SREBP-2 and affects serum cholesterol levels". Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 107 (3): 553–560. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.08.017. ISSN 1096-7192. PMID 22985732.
- ^ Bruice PY (2017). Organic chemistry. Pearson. ISBN 978-0-13-404228-2. OCLC 974910578.
- ^ Tsuda H, Shiraki M, Inoue E, Saito T (August 2016). "Generation of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate from acetate in higher plants: Detection of acetoacetyl CoA reductase- and PHB synthase- activities in rice". Journal of Plant Physiology. 201: 9–16. Bibcode:2016JPPhy.201....9T. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2016.06.007. PMID 27372278.
- ^ Matsumoto K, Tanaka Y, Watanabe T, Motohashi R, Ikeda K, Tobitani K, et al. (October 2013). "Directed evolution and structural analysis of NADPH-dependent Acetoacetyl Coenzyme A (Acetoacetyl-CoA) reductase from Ralstonia eutropha reveals two mutations responsible for enhanced kinetics". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 79 (19): 6134–6139. Bibcode:2013ApEnM..79.6134M. doi:10.1128/aem.01768-13. PMC 3811355. PMID 23913421.
- ^ Taroncher-Oldenburg G, Nishina K, Stephanopoulos G (October 2000). "Identification and analysis of the polyhydroxyalkanoate-specific beta-ketothiolase and acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductase genes in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 66 (10): 4440–4448. Bibcode:2000ApEnM..66.4440T. doi:10.1128/aem.66.10.4440-4448.2000. PMC 92322. PMID 11010896.