| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
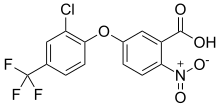
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-[2-Chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-2-nitrobenzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.051.468 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1] | |
| C14H7ClF3NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 361.66 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.573 g/mL |
| Melting point | 155 °C |
| 250 g/L (20 °C) | |
| log P | 1.18 (20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.86 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Acifluorfen is the ISO common name[2] for an organic compound used as an herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase which is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis. Soybeans naturally have a high tolerance to acifluorfen and its salts, via metabolic disposal by glutathione S-transferase.[3][4] It is effective against broadleaf weeds and grasses and is used agriculturally on fields growing soybeans, peanuts, peas, and rice.[5]
- ^ Pesticide Properties Database. "Acifluorfen". University of Hertfordshire. Retrieved 2021-03-03.
- ^ "Compendium of Pesticide Common Names: acifluorfen". BCPC.
- ^ Andrews, Christopher J.; Skipsey, Mark; Townson, Jane K.; Morris, Carol; Jepson, Ian; Edwards, Robert (1997). "Glutathione transferase activities toward herbicides used selectively in soybean". Pesticide Science. 51 (2). Wiley: 213–222. doi:10.1002/(sici)1096-9063(199710)51:2<213::aid-ps622>3.0.co;2-l. ISSN 0031-613X.
- ^ "Registration Review Label Mitigation for Sodium Acifluorfen" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2020-06-02. Retrieved 2021-03-05.
- ^ Acifluorfen, Extension Toxicology Network