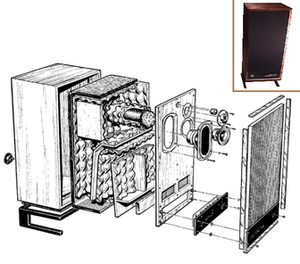
An acoustic transmission line is the use of a long duct, which acts as an acoustic waveguide and is used to produce or transmit sound in an undistorted manner. Technically it is the acoustic analog of the electrical transmission line, typically conceived as a rigid-walled duct or tube, that is long and thin relative to the wavelength of sound present in it.
Examples of transmission line (TL) related technologies include the (mostly obsolete) speaking tube, which transmitted sound to a different location with minimal loss and distortion, wind instruments such as the pipe organ, woodwind and brass which can be modeled in part as transmission lines (although their design also involves generating sound, controlling its timbre, and coupling it efficiently to the open air), and transmission line based loudspeakers which use the same principle to produce accurate extended low bass frequencies and avoid distortion. The comparison between an acoustic duct and an electrical transmission line is useful in "lumped-element" modeling of acoustical systems, in which acoustic elements like volumes, tubes, pistons, and screens can be modeled as single elements in a circuit. With the substitution of pressure for voltage, and volume particle velocity for current, the equations are essentially the same.[2] Electrical transmission lines can be used to describe acoustic tubes and ducts, provided the frequency of the waves in the tube is below the critical frequency, such that they are purely planar.
- ^ Reference speakers imf-electronics.com [dead link]
- ^ Beranek, Leo (1954) Acoustics. American Institute of Physics. ISBN 978-0883184943