| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Acrylic acid[2]
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Prop-2-enoic acid[2] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 635743 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.071 |
| EC Number |
|
| 1817 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
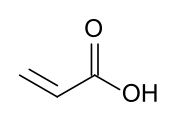
| C3H4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 72.063 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Acrid[3] |
| Density | 1.051 g/mL |
| Melting point | 14 °C (57 °F; 287 K) |
| Boiling point | 141 °C (286 °F; 414 K) |
| Miscible | |
| log P | 0.28[4] |
| Vapor pressure | 3 mmHg[3] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.25 (H2O)[5] |
| Viscosity | 1.3 cP at 20 °C (68 °F) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
    
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H302, H312, H314, H332, H400 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 49.4[6] °C (120.9 °F; 322.5 K) |
| 429 °C (804 °F; 702 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.4–8.02%[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
None[3] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 2 ppm (6 mg/m3) [skin][3] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[3] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
acrylate |
Related carboxylic acids
|
acetic acid propionic acid lactic acid 3-hydroxypropionic acid malonic acid butyric acid crotonic acid |
Related compounds
|
allyl alcohol propionaldehyde acrolein methyl acrylate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: prop-2-enoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than a million tons are produced annually.[7]
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 124.
- ^ a b International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 746. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d e f NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0013". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Acrylic acid_msds".
- ^ Dippy, J. F. J.; Hughes, S. R. C.; Rozanski, A. (1959). "The dissociation constants of some symmetrically disubstituted succinic acids". Journal of the Chemical Society: 2492–2498. doi:10.1039/JR9590002492.
- ^ "ACRYLIC ACID, STABILIZED". Office of Response and Restoration. Retrieved 19 August 2024.
- ^ Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Takahisa; Shimizu, Noboru; Prescher, Günter; Schwind, Helmut; Weiberg, Otto; Marten, Klaus; Greim, Helmut (2003). "Acrylic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_161.pub2. ISBN 3527306730.
