This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (December 2017) |

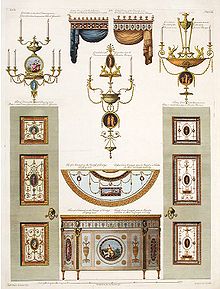
The Adam style (also called Adamesque or the Style of the Brothers Adam) is an 18th-century neoclassical style of interior design and architecture, as practised by Scottish architect William Adam and his sons, of whom Robert (1728–1792) and James (1732–1794) were the most widely known.
The Adam brothers advocated an integrated style for architecture and interiors, with walls, ceilings, fireplaces, furniture, fixtures, fittings and carpets all being designed by the Adams as a single uniform scheme. Their style is commonly known under the mistaken plural "Adams style".
The Adam style found its niche from the late 1760s in upper-class and middle-class residences in 18th-century England, Scotland, Russia (where it was introduced by Scottish architect Charles Cameron), and post-Revolutionary War United States (where it became known as Federal style and took on a variation of its own). The style was superseded from around 1795 onwards by the Regency style and the French Empire style.