In database management, an aggregate function or aggregation function is a function where multiple values are processed together to form a single summary statistic.
Common aggregate functions include:
Others include:
- Nanmean (mean ignoring NaN values, also known as "nil" or "null")
- Stddev
Formally, an aggregate function takes as input a set, a multiset (bag), or a list from some input domain I and outputs an element of an output domain O.[1] The input and output domains may be the same, such as for SUM, or may be different, such as for COUNT.
Aggregate functions occur commonly in numerous programming languages, in spreadsheets, and in relational algebra.
The listagg function, as defined in the SQL:2016 standard[2]
aggregates data from multiple rows into a single concatenated string.
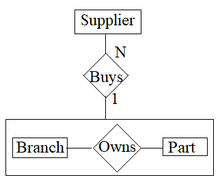
In the entity relationship diagram, aggregation is represented as seen in Figure 1 with a rectangle around the relationship and its entities to indicate that it is being treated as an aggregate entity.[3]
- ^ Jesus, Baquero & Almeida 2011, 2 Problem Definition, pp. 3.
- ^ Winand, Markus (2017-05-15). "Big News in Databases: New SQL Standard, Cloud Wars, and ACIDRain (Spring 2017)". DZone. Archived from the original on 2017-05-27. Retrieved 2017-06-10.
In December 2016, ISO released a new version of the SQL standard. It introduces new features such as row pattern matching, listagg, date and time formatting, and JSON support.
- ^ Elmasri, Ramez (2016). Fundamentals of database systems. Sham Navathe (Seventh ed.). Hoboken, NJ. p. 133. ISBN 978-0-13-397077-7. OCLC 913842106.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)