| Agno River Rio Grande de Pangasinan | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Agno River watershed | |
Agno River mouth | |
| Location | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Regions | |
| Provinces | |
| Cities/municipality | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Mount Data |
| • location | Benguet, Cordillera mountains |
| • coordinates | 16°49′34″N 120°53′17″E / 16.826°N 120.888°E |
| • elevation | 2,090 m (6,860 ft) |
| Mouth | Lingayen Gulf |
• location | Lingayen, Pangasinan, Ilocos Region |
• coordinates | 16°02′17″N 120°12′00″E / 16.03806°N 120.20000°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 248 km (154 mi) |
| Basin size | 5,952 km2 (2,298 sq mi)[1] |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Tarlac River |
 | |
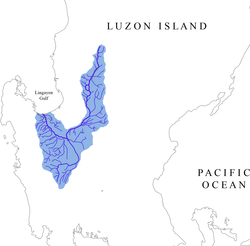
The Agno River, also known as the Pangasinan River, is a river on the island of Luzon in the Philippines. Traversing the provinces of Benguet, Pangasinan, and Tarlac, it is one of the largest river systems in the country, with a drainage area of 5,952 square kilometres (2,298 sq mi).[2][3][4][5]
The river originates in the Cordillera Mountains and empties into the South China Sea via Lingayen Gulf. The river is 248 kilometres (154 mi) long, making it the sixth longest river in the country.[6] Roughly two million people live in the Agno River Valley, making it one of Philippines' larger population clusters.
The river is dammed by three hydroelectric power plants: the Ambuklao Dam in Bokod, the Binga Dam in Itogon, and the San Roque Dam in San Manuel.
- ^ Tuddao, Vicente B. Jr. (September 21, 2011). "Water Quality Management in the Context of Basin Management: Water Quality, River Basin Management and Governance Dynamics in the Philippines" (PDF) (Deck). Department of Environment and Natural Resources. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 29, 2016. Retrieved April 5, 2017.
- ^ "The Agno River Basin". ABS-CBN News. October 23, 2009. Archived from the original on December 3, 2013. Retrieved October 25, 2013.
- ^ "Agno River Basin". PAGASA Regional Service Division. Archived from the original on October 21, 2013. Retrieved October 21, 2013.
- ^ Petr, T., ed. (1985). Inland Fisheries in Multiple-purpose River Basin Planning and Development in Tropical Asian Countries: Three Case Studies. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. p. 20. ISBN 92-5-102327-1.
- ^ Kundel, Jim (April 3, 2008). "Water Profile of Philippines". The Encyclopedia of Earth. Archived from the original on September 21, 2008. Retrieved September 30, 2008.
- ^ Kenneth Kimutai too (July 24, 2018). "Longest Rivers in the Philippines". WorldAtlas. Archived from the original on August 26, 2019. Retrieved September 9, 2019.

