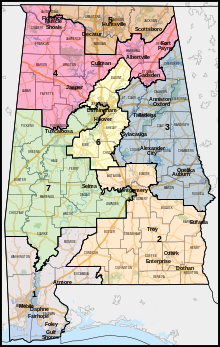

The U.S. state of Alabama is currently divided into seven congressional districts, each represented by a member of the United States House of Representatives.
Since the 1973 redistricting following the 1970 U.S. census, Alabama has had seven congressional districts. This is three fewer districts than the historic high of ten congressional districts just prior to the 1930 census.
In the case of Allen v. Milligan, 599 U.S. 1 (2023), the Supreme Court of the United States held that the state's current map violates section 2 of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 (52 U.S.C. § 10301) and needs to be redrawn with an additional black-majority district. The Alabama Legislature approved another map which also violated the law, but a federal court selected a new map on appeal.[1]
- ^ "Court picks new Alabama congressional map that will likely flip one seat to Democrats". Politico. October 5, 2023. Retrieved October 25, 2023.