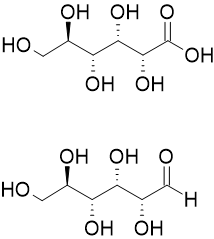
Aldonic acids are sugar acids with the general chemical formula, HO2C(CHOH)nCH2OH. They are obtained by oxidizing the aldehyde (-CHO group) of an aldose to form a carboxylic acid (-COOH group).[1] Aldonic acids are generally found in their ring form. However, these rings do not have a chiral carbon at the terminal end bearing the aldehyde, and they cannot form R−O−R′ linkages between different molecules.[2]
The nomenclature of aldonic acids and their lactones is based on replacing the suffix "-ose" with "onic acid" or "onolactone". Hence, D-glucose is oxidized to D-gluconic acid and D-gluconolactone.[3]
- ^ Gold, Victor, ed. (2019). The IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology: The Gold Book (4 ed.). Research Triangle Park, NC: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). doi:10.1351/goldbook.a00212.
- ^ Sartori, Suélen Karine; Diaz, Marisa Alves Nogueira; Diaz-Muñoz, Gaspar (2021-03-26). "Lactones: Classification, synthesis, biological activities, and industrial applications". Tetrahedron. 84: 132001. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2021.132001. ISSN 0040-4020.
- ^ Robyt, John F. (1998). Essentials of carbohydrate chemistry. Springer advanced texts in chemistry. New York: Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-94951-2.