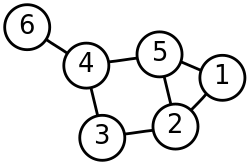
The algebraic connectivity (also known as Fiedler value or Fiedler eigenvalue after Miroslav Fiedler) of a graph G is the second-smallest eigenvalue (counting multiple eigenvalues separately) of the Laplacian matrix of G.[1] This eigenvalue is greater than 0 if and only if G is a connected graph. This is a corollary to the fact that the number of times 0 appears as an eigenvalue in the Laplacian is the number of connected components in the graph. The magnitude of this value reflects how well connected the overall graph is. It has been used in analyzing the robustness and synchronizability of networks.
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Algebraic Connectivity." From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource.