 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Firdapse, Ruzurgi |
| Other names | pyridine-3,4-diamine, 3,4-diaminopyridine, 3,4-DAP |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 93–100%[5] |
| Metabolism | Acetylation to 3-N-acetylamifampridine |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5 hrs (amifampridine) 4 hrs (3-N-acetylamifampridine) |
| Excretion | Kidney (19% unmetabolized, 74–81% 3-N-acetylamifampridine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL |
|
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.201 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
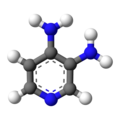
| Formula | C5H7N3 |
| Molar mass | 109.132 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 218 to 220 °C (424 to 428 °F) decomposes |
| Solubility in water | 24 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
Amifampridine is used as a drug, predominantly in the treatment of a number of rare muscle diseases. The free base form of the drug has been used to treat congenital myasthenic syndromes and Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) through compassionate use programs since the 1990s and was recommended as a first line treatment for LEMS in 2006, using ad hoc forms of the drug, since there was no marketed form.
Around 2000 doctors at Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris created a phosphate salt form, which was developed through a series of companies ending with BioMarin Pharmaceutical which obtained European approval in 2009 under the trade name Firdapse, and which licensed the US rights to Catalyst Pharmaceuticals in 2012. As of January 2017, Catalyst and another US company, Jacobus Pharmaceutical, which had been manufacturing and giving it away for free since the 1990s, were both seeking FDA approval for their iterations and marketing rights.
Amifampridine phosphate has orphan drug status in the EU for Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome and Catalyst holds both an orphan designation and a breakthrough therapy designation in the US. In May 2019 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved amifampridine tablets under the trade name Ruzurgi for the treatment of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) in patients 6 to less than 17 years of age. This is the first FDA approval of a treatment specifically for pediatric patients with LEMS. The FDA granted the approval of Ruzurgi to Jacobus Pharmaceutical. The only other treatment approved for LEMS (Firdapse) is only approved for use in adults.[6]
- ^ a b "Ruzurgi APMDS". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 24 September 2021. Retrieved 30 September 2021.
- ^ "Updates to the Prescribing Medicines in Pregnancy database". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 12 May 2022. Retrieved 13 May 2022.
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Firdapse". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Ruzurgi". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
EMAlabel2010was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "FDA approves first treatment for children with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome, a rare autoimmune disorder". fda.gov. Retrieved 2019-05-11.