| Amoebidiidae | |
|---|---|
| |
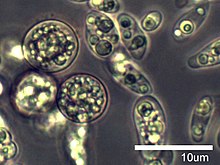
| Amoebidium parasiticum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | Amoebidiidae Lichtenstein 1917 ex Kirk, Canon & David 2001
|
| Genera | |
Amoebidiidae is a family of single-celled eukaryotes, previously thought to be zygomycete fungi belonging to the class Trichomycetes, but molecular phylogenetic analyses[1][2][3] place the family with the opisthokont group Mesomycetozoea[4] (= Ichthyosporea[5]). The family was originally called Amoebidiaceae,[6] and considered the sole family of the fungal order Amoebidiales that included two genera: Amoebidium and Paramoebidium. However, Amoebidiidae is now monogeneric as it was recently emended to include only Amoebidium (and Paramoebidium is now the sole genus of the family Paramoebidiidae).[7] Species of Amoebidium are considered obligate symbionts of freshwater-dwelling arthropod hosts such as midge larvae and water fleas (Daphnia).[8] However, because Amoebidium species attach to the exoskeleton (exterior) of the host and grow in axenic culture, at least some species may be facultative symbionts.[9]
- ^ Benny, G. L., and O'Donnell, K. 2000. Amoebidium parasiticum is a protozoan, not a Trichomycete. Mycologia 92: 1133-1137.
- ^ Ustinova, I, Krienitz, L., and Huss, V. A. R. 2000. Hyaloraphidium curvatum is not a green alga, but a lower fungus; Amoebidium parasiticum is not a fungus, but a member of the DRIPS. Protist 151: 253-262.
- ^ Cafaro, M. 2005. Eccrinales (Trichomycetes) are not fungi, but a clade of protists at the early divergence of animals and fungi. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 35: 21-34.
- ^ Mendoza L, Taylor JW, Ajello L (October 2002). "The class mesomycetozoea: a heterogeneous group of microorganisms at the animal-fungal boundary". Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 56: 315–44. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160950
- ^ Cavalier-Smith, T. 1998. Neomonada and the origin of animals and fungi. In: Coombs GH, Vickerman K, Sleigh MA, Warren A (ed.) Evolutionary relationships among protozoa. Kluwer, London, pp. 375-407.
- ^ Will Karlisle Reeves (2003). "Emendation of the family name Amoebidiaceae (Choanozoa, Mesomycetozoa, Ichthyosporea)". Comparative Parasitology. 70 (1): 78–79. doi:10.1654/1525-2647(2003)070[0078:EOTFNA]2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Reynolds, N.K., M.E. Smith, E.D. Tretter, J. Gause, D. Heeney, M.J. Cafaro, J.F. Smith, S.J. Novak, W.A. Bourland, M.M. White. 2017. Resolving relationships at the animal-fungal divergence: A molecular phylogenetic study of the protist trichomycetes (Ichthyosporea, Eccrinida). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution in press, available online 20Feb.2017. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2017.02.007
- ^ Lichtwardt, R.W. 2001. Trichomycetes: fungi in relationship with insects and other arthropods. In: Symbiosis. J. Seckbach, ed. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, p. 515-588.
- ^ Lichtwardt, R.W., M.J. Cafaro, M.M. White. 2001. The Trichomycetes: Fungal Associates of Arthropods Revised Edition. Published online http://www.nhm.ku.edu/%7Efungi/Monograph/Text/Mono.htm Archived 2017-04-26 at the Wayback Machine