This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2009) |
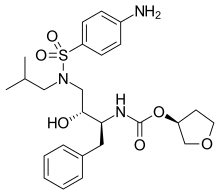 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Agenerase |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a699051 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 7.1–10.6 hours |
| Excretion | <3% renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.262.589 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H35N3O6S |
| Molar mass | 505.63 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Amprenavir (original brand name Agenerase, GlaxoSmithKline) is a protease inhibitor used to treat HIV infection. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration on April 15, 1999, for twice-a-day dosing instead of needing to be taken every eight hours. The convenient dosing came at a price, as the dose required is 1,200 mg, delivered in 8 (eight) very large 150 mg gel capsules or 24 (twenty-four) 50 mg gel capsules twice daily.[1]
It was patented in 1992 and approved for medical use in 1999.[2] Production of amprenavir was discontinued by the manufacturer on December 31, 2004; a prodrug version (fosamprenavir), is available.
- ^ "Agenerase (amprenavir) Capsules. Full Prescribing Information. Section Dosage and Administration" (PDF). US Food and Drug Administration. GlaxoSmithKline and Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc. Retrieved 29 November 2015.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 509. ISBN 9783527607495.