 Amundsen, Hanssen, Hassel, and Wisting at Polheim at the South Pole | |
| Leader | Roald Amundsen |
|---|---|
| Start | Framheim, Great Ice Barrier 19 October 1911 |
| End | Geographic South Pole 14 December 1911 |
| Ships | Fram |
| Crew |
|
| Achievements |
|
| Route | |
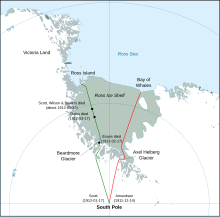 Amundsen's route compared to Scott's | |
The first ever expedition to reach the Geographic South Pole was led by the Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen. He and four other crew members made it to the geographical south pole on 14 December 1911,[n 1] which would prove to be five weeks ahead of the competitive British party led by Robert Falcon Scott as part of the Terra Nova Expedition. Amundsen and his team returned safely to their base, and about a year later heard that Scott and his four companions had perished on their return journey.
Amundsen's initial plans had focused on the Arctic and the conquest of the North Pole by means of an extended drift in an icebound ship. He obtained the use of Fridtjof Nansen's polar exploration ship Fram, and undertook extensive fundraising. Preparations for this expedition were disrupted when, in 1909, the rival American explorers Frederick Cook and Robert Peary each claimed to have reached the North Pole. Amundsen then changed his plan and began to prepare for a conquest of the South Pole; uncertain of the extent to which the public and his backers would support him, he kept this revised objective secret. When he set out in June 1910, he led even his crew to believe they were embarking on an Arctic drift, and revealed their true Antarctic destination only when Fram was leaving their last port of call, Madeira.
Amundsen made his Antarctic base, which he named "Framheim", in the Bay of Whales on the Great Ice Barrier. After months of preparation, depot-laying and a false start that ended in near-disaster, he and his party set out for the pole in October 1911. In the course of their journey they discovered the Axel Heiberg Glacier, which provided their route to the polar plateau and ultimately to the South Pole. The party's mastery of the use of skis and their expertise with sled dogs ensured rapid and relatively trouble-free travel. Other achievements of the expedition included the first exploration of King Edward VII Land and an extensive oceanographic cruise.
The expedition's success was widely applauded, though the story of Scott's heroic failure overshadowed its achievement in the United Kingdom. Amundsen's decision to keep his true plans secret until the last moment was criticised by some. Recent polar historians have more fully recognised the skill and courage of Amundsen's party; the permanent scientific base at the pole bears his name, together with that of Scott.
- ^ Huntford (The Last Place on Earth) 1985, p. 511.
- ^ Amundsen, p. xvii, Vol. I.
Cite error: There are <ref group=n> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=n}} template (see the help page).