| Aortic arch | |
|---|---|
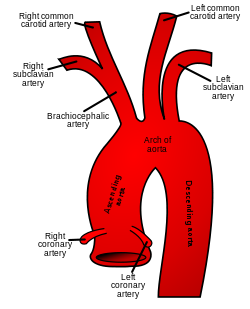 The aortic arch has three branches, the brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian artery. | |
 The aortic arch and its branches shown in situ. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Fourth left pharyngeal arch artery |
| Source | Ascending aorta |
| Branches | Continues as descending aorta, thoracic part |
| Vein | Combination of superior and inferior vena cava |
| Supplies | From its branches, the upper body, arms, head and neck. As a part of the aorta, the entire body, with exception of the respiratory zone of the lung and the heart. |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arcus aortae |
| TA98 | A12.2.04.001 |
| TA2 | 4177 |
| FMA | 3768 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch (English: /eɪˈɔːrtɪk/[1][2]) is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
- ^ OED 2nd edition, 1989, as /eɪ'ɔ:ɹtɪk/.
- ^ Entry "aortic" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.