| Archaeopriapulida Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
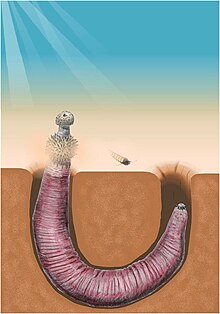
| |
| Reconstruction of the archaeopriapulid Ottoia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Stem group: | Priapulida (?) |
| Class: | †Archaeopriapulida |
| Species[1][2] | |
|
See text | |
Archaeopriapulida is a group of priapulid worms known from Cambrian lagerstätte.[3] The group is closely related to, and very similar to, the modern Priapulids.[4] It is unclear whether it is mono- or polyphyletic.[5] Despite a remarkable morphological similarity to their modern cousins,[6] they fall outside of the priapulid crown group, which is not unambiguously represented in the fossil record until the Carboniferous.[7] In addition to well-preserved body fossils, remains of several archaeopriapulid taxa are known to have been preserved primarily as organic microfossils, such as isolated scalids and pharyngeal teeth.[8][9][10] They are probably closely related or paraphyletic to the palaeoscolecids; the relationship between these basal worms is somewhat unresolved.[5]
- ^ Smith, M. R.; Harvey, T. H. P.; Butterfield, N. J. (2015). "The macro- and microfossil record of the Cambrian priapulid Ottoia" (PDF). Palaeontology. 58 (4): 705–721. doi:10.1111/pala.12168. S2CID 55337080.
- ^ Supplementary information from Smith, M.R.; Harvey, T.H.P.; Butterfield, N.J. (2015). "The macro- and microfossil record of the Cambrian priapulid Ottoia" (PDF). Palaeontology. 58 (4): 705–721. doi:10.1111/pala.12168. S2CID 55337080.
- ^ Conway Morris, S. (1979). "The Burgess Shale (Middle Cambrian) Fauna". Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics. 10: 327–349. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.10.110179.001551.
- ^ Por, F. D. (1983). "Class Seticoronaria and Phylogeny of the Phylum Priapulida". Zoologica Scripta. 12 (4): 267–272. doi:10.1111/j.1463-6409.1983.tb00510.x. S2CID 85091685.
- ^ a b Wills, M. A. (1 April 1998). "Cambrian and Recent Disparity: the Picture from Priapulids". Paleobiology. 24 (2): 177–199. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(1998)024[0177:CARDTP]2.3.CO;2. JSTOR 2401237. S2CID 88647544.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
doi10.1080/00241160410005088was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Budd, G. E.; Jensen, S. (2000). "A critical reappraisal of the fossil record of the bilaterian phyla". Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society. 75 (2): 253–95. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.1999.tb00046.x. PMID 10881389. S2CID 39772232.
- ^ Slater, Ben J.; Harvey, Thomas H. P.; Guilbaud, Romain; Butterfield, Nicholas J. (January 2017). Rahman, Imran (ed.). "A cryptic record of Burgess Shale-type diversity from the early Cambrian of Baltica". Palaeontology. 60 (1): 117–140. doi:10.1111/pala.12273. hdl:2381/38663.
- ^ Smith, Martin R.; Harvey, Thomas H. P.; Butterfield, Nicholas J. (July 2015). Kouchinsky, Artem (ed.). "The macro‐ and microfossil record of the Cambrian priapulid Ottoia". Palaeontology. 58 (4): 705–721. doi:10.1111/pala.12168. ISSN 0031-0239.
- ^ Wernström, Joel Vikberg; Slater, Ben J.; Sørensen, Martin V.; Crampton, Denise; Altenburger, Andreas (2023-08-12). "Geometric morphometrics of macro- and meiofaunal priapulid pharyngeal teeth provides a proxy for studying Cambrian "tooth taxa"". Zoomorphology. doi:10.1007/s00435-023-00617-4. hdl:10037/30213. ISSN 1432-234X.