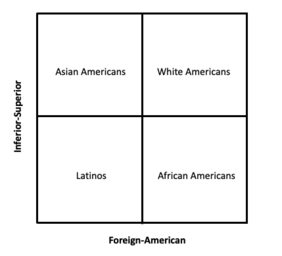
In social psychology, the two axes of subordination is a racial position model that categorizes the four most common racial groups in the United States (Whites, African Americans, Asian Americans, and Latinos) into four different quadrants.[1] The model was first proposed by Linda X. Zou and Sapna Cheryan in the year 2017, and suggests that U.S. racial groups are categorized based on two dimensions: perceived inferiority and perceived cultural foreignness.[1] Support for the model comes from both a target and perceivers perspective in which Whites are seen as superior and American, African Americans as inferior and American, Asian Americans as superior and foreign, and Latinos as inferior and foreign.[1]