| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[(3R,6R,9S,12R,15S)-6-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-9-(2-methylpropyl)-2,5,8,11,14-pentaoxo-12-propan-2-yl-1,4,7,10,13-pentazabicyclo[13.3.0]octadecan-3-yl]acetic acid
| |
| Other names
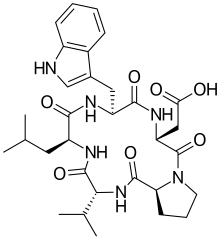
Cyclo(D-trp-D-asp-L-pro-D-val-L-leu)
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C31H42N6O7 | |
| Molar mass | 610.712 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
BQ-123, also known as cyclo(-D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Val-Leu-), is a cyclic pentapeptide that was first isolated from a fermentation broth of Streptomyces misakiensis in 1991.[2] NMR studies indicate that the polypeptide backbone consists of a type II beta turn and an inverse gamma turn.[3][4] The side-chains adopt different orientations depending on the solvent used.[5][6] The proline carbonyl oxygen atom located at the onset of a beta turn is a sodium ion binding site.[7] It has a high affinity for sodium ions and can coordinate up to three of them.[8] Studies have shown that BQ123 is effective in reversing Ischemia-induced acute renal failure, and it has been suggested that this might be because BQ123 increases reabsorption of sodium ions in the proximal tubule cells.[9][10][11][12][13]
BQ-123 is a selective ETA endothelin receptor antagonist.[1][14] As such, it is used as a biochemical tool in the study of endothelin receptor function. BQ-123 works as an ET-1 antagonist by reversing already established contractions to ET-1. This indicates that BQ-123 can work as an antagonist to remove ET-1 from its receptor (ETA).[15]
- ^ a b BQ-123 at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ Ihara M, Fukuroda T, Saeki T, Nishikibe M, Kojiri K, Suda H, Yano M (July 1991). "An endothelin receptor (ETA) antagonist isolated from Streptomyces misakiensis". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 178 (1): 132–7. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(91)91789-F. PMID 1648907.
- ^ Atkinson RA, Pelton JT (January 1992). "Conformational study of cyclo[D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Val-Leu], an endothelin-A receptor-selective antagonist". FEBS Letters. 296 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(92)80390-3. PMID 1309703.
- ^ Krystek SR, Bassolino DA, Bruccoleri RE, Hunt JT, Porubcan MA, Wandler CF, Andersen NH (March 1992). "Solution conformation of a cyclic pentapeptide endothelin antagonist. Comparison of structures obtained from constrained dynamics and conformational search". FEBS Letters. 299 (3): 255–61. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(92)80127-3. PMID 1544503.
- ^ Gonnella NC, Zhang X, Jin Y, Prakash O, Paris CG, Kolossváry I, et al. (May 1994). "Solvent effects on the conformation of cyclo(-D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Val-Leu-). An NMR spectroscopy and molecular modeling study". International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research. 43 (5): 454–62. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3011.1994.tb00544.x. PMID 8070969.
- ^ Bean JW, Peishoff CE, Kopple KD (September 1994). "Conformations of cyclic pentapeptide endothelin receptor antagonists". International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research. 44 (3): 223–32. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3011.1994.tb00164.x. PMID 7822098.
- ^ Ngoka LC, Gross ML (February 2000). "Location of alkali metal binding sites in endothelin A selective receptor antagonists, cyclo(D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Val-Leu) and cyclo(D-Trp-D-Asp-Pro-D-Ile-Leu), from multistep collisionally activated decompositions". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 35 (2): 265–76. Bibcode:2000JMSp...35..265N. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9888(200002)35:2<265::AID-JMS946>3.0.CO;2-#. PMID 10679990.
- ^ Ngoka LC, Gross ML (January 1999). "Novel sodium binding properties of some cyclopentapeptide endothelin A selective receptor antagonists: electrospray and fast-atom-bombardment mass spectrometric studies". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 254 (3): 713–9. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9772. PMID 9920807.
- ^ Büyükgebiz O, Aktan AO, Haklar G, Yalçin AS, Yeğen C, Yalin R, Ercan ZS (1996). "BQ-123, a specific endothelin (ETA) receptor antagonist, prevents ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation". Transplant International. 9 (3): 201–7. doi:10.1007/BF00335386. PMID 8723187. S2CID 39612393.
- ^ Clozel M, Watanabe H (1993). "BQ-123, a peptidic endothelin ETA receptor antagonist, prevents the early cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage after intracisternal but not intravenous injection". Life Sciences. 52 (9): 825–34. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(93)90081-d. PMID 8437512.
- ^ Clavell AL, Stingo AJ, Margulies KB, Brandt RR, Burnett JC (March 1995). "Role of endothelin receptor subtypes in the in vivo regulation of renal function". The American Journal of Physiology. 268 (3 Pt 2): F455-60. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.1995.268.3.F455. PMID 7900845.
- ^ Gellai M, Jugus M, Fletcher T, DeWolf R, Nambi P (February 1994). "Reversal of postischemic acute renal failure with a selective endothelinA receptor antagonist in the rat". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 93 (2): 900–6. doi:10.1172/JCI117046. PMC 293964. PMID 8113422.
- ^ Mino N, Kobayashi M, Nakajima A, Amano H, Shimamoto K, Ishikawa K, et al. (October 1992). "Protective effect of a selective endothelin receptor antagonist, BQ-123, in ischemic acute renal failure in rats". European Journal of Pharmacology. 221 (1): 77–83. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(92)90774-x. PMID 1459192.
- ^ Ishikawa K, Fukami T, Nagase T, Fujita K, Hayama T, Niiyama K, et al. (May 1992). "Cyclic pentapeptide endothelin antagonists with high ETA selectivity. Potency- and solubility-enhancing modifications". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 35 (11): 2139–42. doi:10.1021/jm00089a028. PMID 1317926.
- ^ Berrazueta JR, Bhagat K, Vallance P, MacAllister RJ (December 1997). "Dose- and time-dependency of the dilator effects of the endothelin antagonist, BQ-123, in the human forearm". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 44 (6): 569–71. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.1997.t01-1-00631.x. PMC 2042881. PMID 9431833.