| bZIP transcription factor | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
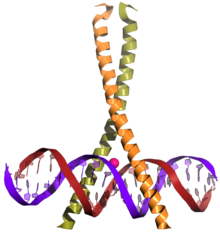 CREB (top) is a transcription factor capable of binding DNA via the bZIP domain (bottom) and regulating gene expression. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | bZIP_1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00170 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR011616 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00036 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1ysa / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| CDD | cd14686 | ||||||||
| Membranome | 235 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain (bZIP domain) is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required to hold together (dimerize) two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic amino acids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containing this domain are transcription factors.[1][2]
- ^ Ellenberger T (1994). "Getting a grip in DNA recognition: structures of the basic region leucine zipper, and the basic region helix-loop-helix DNA-binding domains". Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 4 (1): 12–21. doi:10.1016/S0959-440X(94)90054-X.
- ^ Hurst HC (1995). "Transcription factors 1: bZIP proteins". Protein Profile. 2 (2): 101–68. PMID 7780801.