| Battle of Al Faw | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the 2003 invasion of Iraq | |||||||||
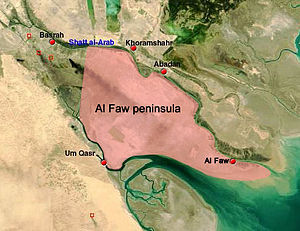 Map of Iraq's Al-Faw Peninsula, along the Iran–Iraq border | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| ~3,500 troops | 1,000+ troops | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| 19 killed (15 British, 4 American) |
150+ killed 440 captured | ||||||||


The Battle of Al Faw began on 20 March 2003 and continued for four days, as part of the 2003 invasion of Iraq.
One of the initial objectives of the Coalition was to capture every GOPLAT (gas and oil platform) in the Al-Faw Peninsula before they could be sabotaged or destroyed by the Iraqi military. Doing so would also deny Iraq the ability to cause another ecological disaster, as it had done with the Kuwait oil fires and the Persian Gulf oil spill in 1991. By seizing the country's coast, the Coalition would also ensure a quicker takeover of Iraqi oil production.
The 3 Commando Brigade of the British Armed Forces would also capture Umm Qasr at the same time, so that Umm Qasr Port—the only deep water port in Iraq—could be used to bring in heavy military supplies once Khawr Abd Allah was cleared by the Mine Counter Measures Task Group. The 15th Marine Expeditionary Unit of the United States Marine Corps was placed under the command of 3 Commando Brigade in order to provide the necessary force for capturing both targets.