| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
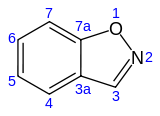
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-Benzoxazole | |||
| Other names
Benzo[d]isoxazole; Indoxazine
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 2154 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.440 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C7H5NO | |||
| Molar mass | 119.123 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.18 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 35 to 38 °C (95 to 100 °F; 308 to 311 K) (at 2.67 hPa) 101-102 °C (at 2 kPa) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| Flash point | 58 °C (136 °F; 331 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
1,2-Benzisoxazole is an aromatic organic compound with a molecular formula C7H5NO containing a benzene-fused isoxazole ring structure.[1][2] The compound itself has no common applications; however, functionalized benzisoxazoles and benzisoxazoyls have a variety of uses, including pharmaceutical drugs such as some antipsychotics (including risperidone, paliperidone, ocaperidone, and iloperidone) and the anticonvulsant zonisamide.
Its aromaticity makes it relatively stable;[3] however, it is only weakly basic.
- ^ Katritzky, A. R.; Pozharskii, A. F. (2000). Handbook of Heterocyclic Chemistry (2nd ed.). Academic Press. ISBN 0080429882.
- ^ Clayden, J.; Greeves, N.; Warren, S.; Wothers, P. (2001). Organic Chemistry. Oxford, Oxfordshire: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-850346-6.
- ^ Domene, Carmen; Jenneskens, Leonardus W.; Fowler, Patrick W. (2005). "Aromaticity of anthranil and its isomers, 1,2-benzisoxazole and benzoxazole". Tetrahedron Letters. 46 (23): 4077–4080. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.04.014. hdl:1874/14837. ISSN 0040-4039.

