
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bicyclo[4.2.0]octa-1,3,5-triene | |
| Other names
Benzocyclobutane
BCB Benzocyclobutene (not in accordance with IUPAC nomenclature) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.161.355 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8 | |
| Molar mass | 104.152 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.957 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 150 °C (302 °F; 423 K) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.541 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
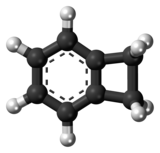
Benzocyclobutene (BCB) is a benzene ring fused to a cyclobutane ring. It has chemical formula C8H8.[1]
BCB is frequently used to create photosensitive polymers. BCB-based polymer dielectrics may be spun on or applied to various substrates for use in Micro Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) and microelectronics processing. Applications include wafer bonding, optical interconnects, low-κ dielectrics, or even intracortical neural implants.