 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 50–70% |
| Metabolism | Unknown |
| Elimination half-life | 35–40 minutes |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
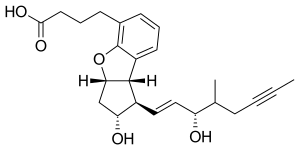
| Formula | C24H30O5 |
| Molar mass | 398.499 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Beraprost is a pharmaceutical drug used in several Asian countries, including Japan and South Korea, as a vasodilator and antiplatelet agent.[1] It is classified as a prostacyclin analog.[1][2]
It has been studied for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension and for use in avoiding reperfusion injury.
- ^ a b "Beraprost". drugs.com.
- ^ Melian EB, Goa KL (2002). "Beraprost: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of peripheral arterial disease and pulmonary arterial hypertension". Drugs. 62 (1): 107–33. doi:10.2165/00003495-200262010-00005. PMID 11790158.