| Biceps femoris | |
|---|---|
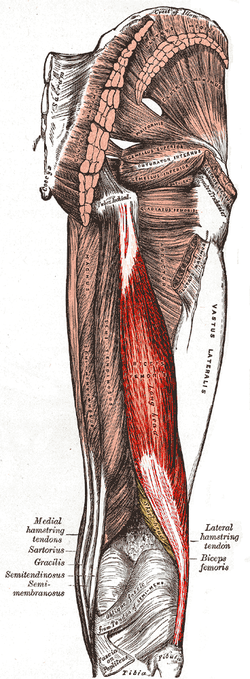 Posterior view of right leg. Long head of muscle highlighted in red, short head (yellow) labeled in the lower part of the image | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Tuberosity of the ischium, linea aspera, femur |
| Insertion | The head of the fibula which articulates with the back of the lateral tibial condyle |
| Artery | Deep femoral artery, perforating arteries; long head of biceps femoris: perforating branches from profunda femoris artery |
| Nerve | Long head: tibial nerve short head: common fibular nerve |
| Actions | Flexes knee joint, laterally rotates knee joint (when knee is flexed), extends hip joint (long head only) |
| Antagonist | Quadriceps muscle |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus biceps femoris |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.032 |
| TA2 | 2638 |
| FMA | 22356 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The biceps femoris (/ˈbaɪsɛps ˈfɛmərɪs/) is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion (but not hip extension)[1] and is activated by a separate nerve (the peroneal, as opposed to the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve).
- ^ Rodgers, Cooper D.; Raja, Avais. StatPearls - Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Hamstring Muscle. StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 25 February 2023. Retrieved 5 April 2023.