| Big brown bat | |
|---|---|

| |
| A big brown bat on a rock | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Vespertilionidae |
| Genus: | Eptesicus |
| Species: | E. fuscus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eptesicus fuscus (Beauvois, 1796)
| |
| |
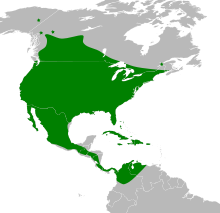
| Range map | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The big brown bat (Eptesicus fuscus) is a species of vesper bat distributed widely throughout North America, the Caribbean, and the northern portion of South America. It was first described as a species in 1796. Compared to other microbats, the big brown bat is relatively large, weighing 15–26 g (0.53–0.92 oz) and possessing a wingspan of 32.5–35 cm (12.8–13.8 in).
Big brown bats are insectivorous, consuming a diverse array of insects, particularly night-flying insects, but especially beetles.[4] Some of the beetles it consumes are serious agricultural pests, including cucumber beetles. They are nocturnal, foraging for prey at night and roosting in sheltered areas during the day such as caves, tunnels, tree cavities, and human structures. Their breeding season is in the fall, shortly before their annual hibernation. After hibernation ends in the spring, females form maternity colonies for giving birth to young. Oftentimes only one offspring is produced per litter, though twins are common in the Eastern US. Lifespans of 6.5 years are considered average.
The big brown bat occurs widely throughout the US, Canada, Central America, and the Caribbean. Its range extends into parts of South America, found as far south as Colombia and Venezuela. It is adaptable to many habitats and is considered a generalist species. The big brown bat is not considered at risk for extinction, and is evaluated as the lowest conservation priority by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
While some other bat species in its range have experienced dramatic population declines due to the fungal disease white-nose syndrome, the big brown bat is relatively resistant to the effects of the disease, and some populations have even increased since the syndrome arrived in North America. Like all bats in the US, the big brown bat can be impacted by rabies, though some individuals have immunity against the virus. Even though sick bats are more likely to be submitted for testing, in 2011, only 3.8%[5] of submitted big brown bats were positive for the rabies virus. Bat boxes are sometimes used to attract them as they are an agriculturally valuable species.
- ^ Miller, B.; Reid, F.; Arroyo-Cabrales, J.; Cuarón, A.D.; de Grammont, P.C. (2016). "Eptesicus fuscus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T7928A22118197. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T7928A22118197.en. Retrieved 20 February 2022.
- ^ Wood Grinnell, Hilda (1918). A Synopsis of the Bats of California. Vol. 17. University of California Press. p. 318.
- ^ Hutcheon, James M.; Kirsch, John A. W. (2006). "A moveable face: Deconstructing the Microchiroptera and a new classification of extant bats". Acta Chiropterologica. 8: 8. doi:10.3161/1733-5329(2006)8[1:AMFDTM]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1733-5329. S2CID 85948117.
- ^ "Big Brown Bat – Shenandoah National Park (U.S. National Park Service)". National Park Service. Retrieved 9 December 2019.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Birhane 2017was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
