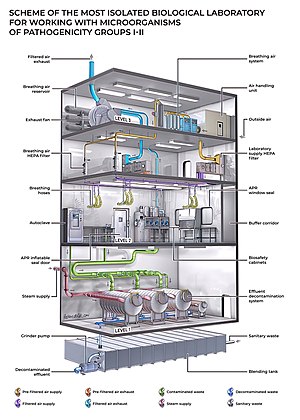
A biosafety level (BSL), or pathogen/protection level, is a set of biocontainment precautions required to isolate dangerous biological agents in an enclosed laboratory facility. The levels of containment range from the lowest biosafety level 1 (BSL-1) to the highest at level 4 (BSL-4). In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have specified these levels in a publication referred to as BMBL.[2] In the European Union, the same biosafety levels are defined in a directive.[3] In Canada the four levels are known as Containment Levels.[4] Facilities with these designations are also sometimes given as P1 through P4 (for pathogen or protection level), as in the term P3 laboratory.[5]
At the lowest level of biosafety, precautions may consist of regular hand-washing and minimal protective equipment. At higher biosafety levels, precautions may include airflow systems, multiple containment rooms, sealed containers, positive pressure personnel suits, established protocols for all procedures, extensive personnel training, and high levels of security to control access to the facility. Health Canada reports that world-wide until 1999 there were recorded over 5,000 cases of accidental laboratory infections and 190 deaths.[6]
- ^ "Integrated Research Facility". niaid.nih.gov. NIAID. Archived from the original on 28 November 2014. Retrieved 14 November 2014.
- ^ Chosewood LC, Wilson DE, eds. (2009). Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories (5th ed.). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ISBN 978-0-1608-5042-4. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ^ Directive 2000/54/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 September 2000 on the protection of workers from risks related to exposure to biological agents at work (seventh individual directive within the meaning of Article 16(1) of Directive 89/391/EEC)
- ^ Canada, Public Health Agency of. "Chapter 2: The Laboratory Biosafety Guidelines: 3rd Edition 2004 – Biological safety – Canada.ca". www.canada.ca. Archived from the original on 23 February 2018. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- ^ Laboratory Safety Monograph: A Supplement to the NIH Guidelines for Recombinant DNA Research. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, Office of Research Safety. 1978. passim.
- ^ "Biosafety at Ryerson" (PDF). Ryerson University Facilities Management and Design. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.