Bipyridines are a family of organic compounds with the formula (C5H4N)2, consisting of two pyridyl (C5H4N) rings. Pyridine is an aromatic nitrogen-containing heterocycle. The bipyridines are all colourless solids, which are soluble in organic solvents and slightly soluble in water. Bipyridines, especially the 4,4' isomer, are mainly of significance in pesticides.[1]
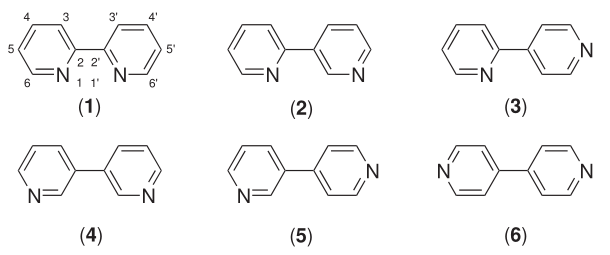
Six isomers of bipyridine exist, but two are prominent. 2,2′-bipyridine, also known as bipyridyl, dipyridyl, and dipyridine, is a popular ligand in coordination chemistry[2][3]
- ^ Shimizu, Shinkichi; Watanabe, Nanao; Kataoka, Toshiaki; Shoji, Takayuki; Abe, Nobuyuki; Morishita, Sinji; Ichimura, Hisao (2000). "Pyridine and Pyridine Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_399. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ McCleverty, Jon A.; Meyer, Thomas J., eds. (2004). Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry II: from Biology to Nanotechnology (1st ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier Pergamon. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-08-043748-4.
- ^ Kaes, Christian; Katz, Alexander; Hosseini, Mir Wais (2000). "Bipyridine: The Most Widely Used Ligand. A Review of Molecules Comprising at Least Two 2,2'-Bipyridine Units". Chemical Reviews. 100 (10): 3553–3590. doi:10.1021/cr990376z. PMID 11749322.