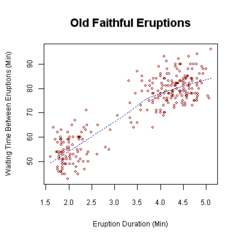
Bivariate analysis is one of the simplest forms of quantitative (statistical) analysis.[1] It involves the analysis of two variables (often denoted as X, Y), for the purpose of determining the empirical relationship between them.[1]
Bivariate analysis can be helpful in testing simple hypotheses of association. Bivariate analysis can help determine to what extent it becomes easier to know and predict a value for one variable (possibly a dependent variable) if we know the value of the other variable (possibly the independent variable) (see also correlation and simple linear regression).[2]
Bivariate analysis can be contrasted with univariate analysis in which only one variable is analysed.[1] Like univariate analysis, bivariate analysis can be descriptive or inferential. It is the analysis of the relationship between the two variables.[1] Bivariate analysis is a simple (two variable) special case of multivariate analysis (where multiple relations between multiple variables are examined simultaneously).[1]
- ^ a b c d e Earl R. Babbie, The Practice of Social Research, 12th edition, Wadsworth Publishing, 2009, ISBN 0-495-59841-0, pp. 436–440
- ^ Bivariate Analysis, Sociology Index