| Black-footed mongoose | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Herpestidae |
| Genus: | Bdeogale |
| Species: | B. nigripes
|
| Binomial name | |
| Bdeogale nigripes Pucheran, 1855
| |
| |
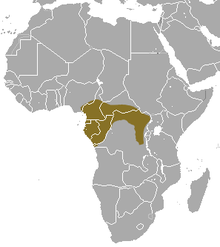
| Black-footed mongoose range | |
The black-footed mongoose (Bdeogale nigripes) is a mongoose species native to Central Africa, where it inhabits deep deciduous forests from eastern Nigeria to the southern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008.[1] It is omnivorous and feeds on ants, termites, Orthoptera, small rodents, frogs, lizards and fruits.[2][3] It is mostly solitary and nocturnal.[4]
Results of genetic and morphological analyses indicate that the black-footed mongoose is closely related to Jackson's mongoose, which is considered conspecific.[5]
- ^ a b Angelici, F.M.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Bdeogale nigripes". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41592A45205243. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41592A45205243.en.
- ^ Ray, J.; Sunquist, M. (2001). "Trophic relations in a community of African rainforest carnivores". Oecologia. 127 (3): 395–408. Bibcode:2001Oecol.127..395R. doi:10.1007/s004420000604. PMID 28547110. S2CID 39830155.
- ^ Angelici, F. M. (2014). "Dietary habits of the Black-legged mongoose Bdeogale nigripes (Mammalia: Carnivora) in the rainforest of Southeastern Nigeria". Italian Journal of Zoology. 81 (4): 544–551. doi:10.1080/11250003.2014.940005. S2CID 84242728.
- ^ Van Rompaey, H.; Colyn, M. (2013). "Bdeogale nigripes Black-legged Mongoose". In J. Kingdon, J.; Hoffmann, M. (eds.). The Mammals of Africa. V. Carnivores, Pangolins, Equids and Rhinoceroses. London, UK: Bloomsbury. pp. 326–328. ISBN 9781408189962.
- ^ Perez, M.; Li, B.; Tillier, A.; Cruaud, A.; Veron, G. (2006). "Systematic relationships of the bushy-tailed and black-footed mongooses (genus Bdeogale, Herpestidae, Carnivora) based on molecular, chromosomal and morphological evidence". Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research. 44 (3): 251–259. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0469.2006.00359.x.
