This article has problems which may render some text or images unreadable or difficult to read in dark mode. Desktop readers can switch to light mode temporarily using the eyeglasses icon at the top of the page. |
| Communication protocol | |
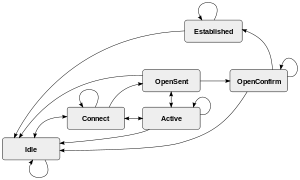 BGP state machine | |
| Abbreviation | BGP |
|---|---|
| Purpose | exchange Internet Protocol routing information |
| Introduction | June 1, 1989[1] |
| Based on | EGP |
| OSI layer | Application layer |
| Port(s) | tcp/179 |
| RFC(s) | § Standards documents |
| Internet protocol suite |
|---|
| Application layer |
| Transport layer |
| Internet layer |
| Link layer |
| Internet history timeline |
|
Early research and development:
Merging the networks and creating the Internet:
Commercialization, privatization, broader access leads to the modern Internet:
Examples of Internet services:
|
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems (AS) on the Internet.[2] BGP is classified as a path-vector routing protocol,[3] and it makes routing decisions based on paths, network policies, or rule-sets configured by a network administrator.
BGP used for routing within an autonomous system is called Interior Border Gateway Protocol (iBGP). In contrast, the Internet application of the protocol is called Exterior Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP).
- ^ "History for rfc1105". IETF. June 1989. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ^ "BGP: Border Gateway Protocol Explained". Orbit-Computer Solutions.Com. Archived from the original on 2013-09-28. Retrieved 2013-10-08.
- ^ Sobrinho, João Luís (2003). "Network Routing with Path Vector Protocols: Theory and Applications" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2010-07-14. Retrieved March 16, 2018.