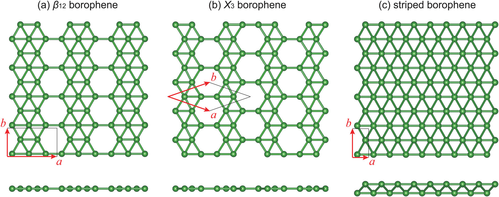
Borophene is a crystalline atomic monolayer of boron, i.e., it is a two-dimensional allotrope of boron and also known as boron sheet. First predicted by theory in the mid-1990s,[1] different borophene structures were experimentally confirmed in 2015.[2][3]
- ^ Boustani, Ihsan (January 1997). "New quasi-planar surfaces of bare boron". Surface Science. 370 (2–3): 355–363. Bibcode:1997SurSc.370..355B. doi:10.1016/S0039-6028(96)00969-7.
- ^ Mannix, A. J.; Zhou, X.-F.; Kiraly, B.; Wood, J. D.; Alducin, D.; Myers, B. D.; Liu, X.; Fisher, B. L.; Santiago, U.; Guest, J. R.; et al. (December 17, 2015). "Synthesis of borophenes: Anisotropic, two-dimensional boron polymorphs". Science. 350 (6267): 1513–1516. Bibcode:2015Sci...350.1513M. doi:10.1126/science.aad1080. PMC 4922135. PMID 26680195.
- ^ Feng, Baojie; Zhang, Jin; Zhong, Qing; Li, Wenbin; Li, Shuai; Li, Hui; Cheng, Peng; Meng, Sheng; Chen, Lan; Wu, Kehui (March 28, 2016). "Experimental realization of two-dimensional boron sheets". Nature Chemistry. 8 (6): 563–568. arXiv:1512.05029. Bibcode:2016NatCh...8..563F. doi:10.1038/nchem.2491. PMID 27219700. S2CID 19475989.