| Brain injury | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Brain damage, neurotrauma |
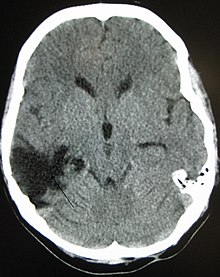 | |
| A CT of the head years after a traumatic brain injury showing an empty space where the damage occurred, marked by the arrow | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Symptoms | Depending on brain area injured |
| Types | Acquired brain injury (ABI), traumatic brain injury (TBI), focal or diffuse, primary and secondary |
Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
A common category with the greatest number of injuries is traumatic brain injury (TBI) following physical trauma or head injury from an outside source, and the term acquired brain injury (ABI) is used in appropriate circles to differentiate brain injuries occurring after birth from injury, from a genetic disorder (GBI), or from a congenital disorder (CBI).[1] Primary and secondary brain injuries identify the processes involved, while focal and diffuse brain injury describe the severity and localization.[citation needed]
Impaired function of affected areas can be compensated through neuroplasticity by forming new neural connections.
- ^ "What is an Acquired Brain Injury?" (PDF). Headway. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-07-05. Retrieved 19 September 2016.