 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lexotan, Lexotanil, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Addiction liability | High[1] |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 84% |
| Protein binding | 70% |
| Metabolism | Liver: P450 |
| Metabolites | 3-hydroxybromazepam |
| Elimination half-life | 12–20 hours (avg. 17hr)[3] |
| Excretion | Urine 69%, as metabolites[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.748 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
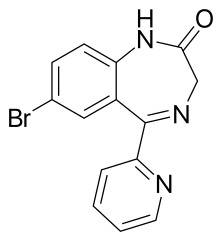
| Formula | C14H10BrN3O |
| Molar mass | 316.158 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Bromazepam, sold under many brand names, is a benzodiazepine. It is mainly an anti-anxiety agent with similar side effects to diazepam. In addition to being used to treat anxiety or panic states, bromazepam may be used as a premedicant prior to minor surgery. Bromazepam typically comes in doses of 3 mg and 6 mg tablets.[4]
It was patented in 1961 by Roche and approved for medical use in 1974.[5]
- ^ a b "Bromazepam: Uses, Interactions, Mechanism of Action". DrugBank Online. Retrieved 2024-02-25.
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ "Lexotan (bromazepam) Product Insert" (PDF). Roche. 23 October 2012.
- ^ "Bromazepam". Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS). Australian Government - Department of Health. Retrieved 23 March 2014.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 53X. ISBN 9783527607495.