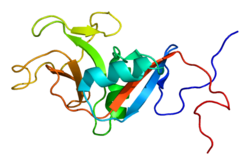
CD23, also known as Fc epsilon RII, or FcεRII, is the "low-affinity" receptor for IgE, an antibody isotype involved in allergy and resistance to parasites, and is important in regulation of IgE levels. Unlike many of the antibody receptors, CD23 is a C-type lectin. It is found on mature B cells, activated macrophages, eosinophils, follicular dendritic cells, and platelets.
There are two forms of CD23: CD23a and CD23b. CD23a is present on follicular B cells, whereas CD23b requires IL-4 to be expressed on T-cells, monocytes, Langerhans cells, eosinophils, and macrophages.[5]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000104921 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000005540 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Lichtman AH, Abbas AK (2003). Cellular and molecular immunology. Philadelphia: Saunders. pp. 324–325. ISBN 0-7216-0008-5.