
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cadmium(II) iodide
| |
| Other names
Cadmium diiodide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.294 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CdI2 | |
| Molar mass | 366.22 g/mol |
| Appearance | white to pale yellow crystals |
| Density | 5.640 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 387 °C (729 °F; 660 K) |
| Boiling point | 742 °C (1,368 °F; 1,015 K) |
| 787 g/L (0 °C) 847 g/L (20 °C) 1250 g/L (100 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, acetone, ether and ammonia |
| -117.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |
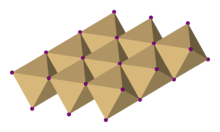
| Structure | |
| Trigonal, hP3, space group P3m1, No. 164 | |
| octahedral | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H301, H331, H351, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P280, P301+P330+P331, P304+P340, P310, P311, P403+P233 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
[1910.1027] TWA 0.005 mg/m3 (as Cd)[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [9 mg/m3 (as Cd)][1] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
cadmium fluoride cadmium chloride cadmium bromide |
Other cations
|
zinc iodide mercury(II) iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cadmium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate.[2] It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects.
