 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cafcit, Gencebok, Cafnea, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous (IV) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.125.472 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
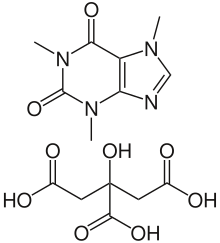
| Formula | C14H18N4O9 |
| Molar mass | 386.317 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Caffeine citrate, sold under the brand name Cafcit among others, is a medication used to treat a lack of breathing in premature babies.[5] Specifically it is given to babies who are born at less than 35 weeks or weigh less than 2 kilograms (4.4 lb) once other causes are ruled out.[6] It is given by mouth or slow injection into a vein.[5]
Side effects can include problems feeding, increased heart rate, low blood sugar, necrotizing enterocolitis, and kidney problems.[5][6] Testing blood caffeine levels is occasionally recommended.[5] Although it is often referred to as a citric acid salt of caffeine,[7] as implied by its name, caffeine citrate in fact consists of cocrystals of the two components.[8] Caffeine citrate is in the xanthine family of medication.[6] It works by stimulating the respiratory centers in the brain.[5]
Caffeine was discovered in 1819.[9] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[10] The intravenous form may also be taken by mouth.[11]
In June 2020, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) recommended the approval of Gencebok.[12] It was approved for use in the European Union in August 2020.[3]
- ^ "Regulatory Decision Summary - Peyona". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 5 June 2022.
- ^ "Cafcit- caffeine citrate injection". DailyMed. 3 January 2020. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- ^ a b "Gencebok EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 19 June 2020. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- ^ "Gencebok Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. Retrieved 3 March 2023.
- ^ a b c d e "Caffeine; Caffeine and Sodium Benzoate Injection; Caffeine Citrate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 16 July 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. p. 485. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ^ Donn SM, Sinha SK (2012). Manual of Neonatal Respiratory Care. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 457. ISBN 9781461421559. Archived from the original on 30 December 2016.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Smit_2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Brown N (2015). In Silico Medicinal Chemistry: Computational Methods to Support Drug Design. Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 20. ISBN 9781782621638. Archived from the original on 29 December 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ Ainsworth SB (2014). Neonatal Formulary: Drug Use in Pregnancy and the First Year of Life (7 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 120. ISBN 9781118819517. Archived from the original on 30 December 2016.
- ^ "Gencebok: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 25 June 2020. Archived from the original on 27 June 2020. Retrieved 26 June 2020.