| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Tetrachloromethane | |||
| Other names
Benzinoform
carbon(IV) chloride carbon tet Carboneum Tetrachloratum / Carbonei tetrachloridum Carboneum Chloratum / Carbonei chlorurum chloride of carbon Freon-10 Halon-104 methane tetrachloride methyl tetrachloride Necatorina perchloromethane Refrigerant-10 Tetrachloretum Carbonicum Tetrachlorocarbon Tetraform Tetrasol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | CTC, TCM, PCM, R-10 | ||
| 1098295 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.239 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 2347 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1846 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
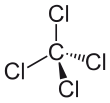
| CCl4 | |||
| Molar mass | 153.81 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Odor | chloroform-like odor | ||
| Density |
| ||
| Melting point | −22.92 °C (−9.26 °F; 250.23 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 76.72 °C (170.10 °F; 349.87 K) | ||
| |||
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform, benzene, naphtha, CS2, formic acid | ||
| log P | 2.64 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 11.94 kPa at 20 °C | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
2.76×10−2 atm·m3/mol | ||
| −66.60×10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Thermal conductivity | 0.1036 W/m·K (300 K)[1] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.4607 | ||
| Viscosity | 0.86 mPa·s[2] | ||
| 0 D | |||
| Structure | |||
| Monoclinic | |||
| Tetragonal | |||
| Tetrahedral | |||
| 0 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
132.6 J/mol·K | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
214.39 J/mol·K | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−95.6 kJ/mol | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−87.34 kJ/mol[3] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
extremely toxic to the liver and kidneys, potential occupational carcinogen, harmful to the ozone layer | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H301, H302, H311, H331, H351, H372, H412, H420 | |||
| P201, P202, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P308+P313, P311, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+P233, P405, P501, P502 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | non-flammable | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
7749 mg/kg (oral, mouse); 5760 mg/kg (oral, rabbit); 2350 mg/kg (oral, rat)[5] | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
| ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
| ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 10 ppm C 25 ppm 200 ppm (5-minute maximum peak in any 4 hours)[4] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca ST 2 ppm (12.6 mg/m3) [60-minute][4] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
200 ppm[4] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0024 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Carbon tetrafluoride Carbon tetrabromide Carbon tetraiodide | ||
Other cations
|
Silicon tetrachloride Germanium tetrachloride Tin tetrachloride Lead tetrachloride | ||
Related chloromethanes
|
Chloromethane Dichloromethane Trichloromethane | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Carbon tetrachloride (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as carbon tet for short and tetrachloromethane, also recognised by the IUPAC), is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CCl4. It is a non-flammable, dense, colourless liquid with a "sweet" chloroform-like odour that can be detected at low levels. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants, an anthelmintic and a cleaning agent, but has since been phased out because of environmental and safety concerns. Exposure to high concentrations of carbon tetrachloride can affect the central nervous system and degenerate the liver and kidneys. Prolonged exposure can be fatal.
- ^ Touloukian, Y.S., Liley, P.E., and Saxena, S.C. Thermophysical properties of matter - the TPRC data series. Volume 3. Thermal conductivity - nonmetallic liquids and gases. Data book. 1970.
- ^ Reid, Robert C.; Prausnitz, John M.; Poling, Bruce E. (1987), The Properties of Gases and Liquids, McGraw-Hill Book Company, p. 442, ISBN 0-07-051799-1
- ^ "Carbon tetrachloride" (PDF). Cheméo. Retrieved 14 Jun 2022.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0107". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Carbon Tetrachloride MSDS from Fisher Scientific
- ^ a b "Carbon tetrachloride". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).